New milestones for USA Fibre deployments
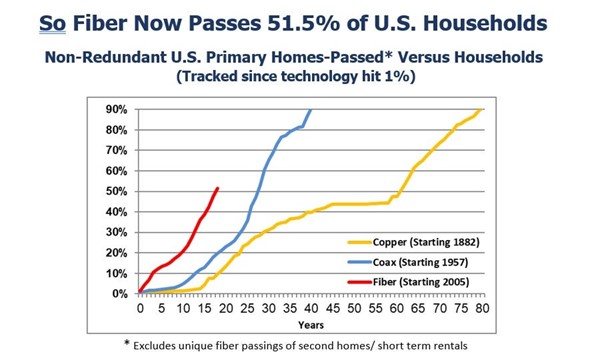
Fiber broadband deployment reached record levels in 2023. Nine million new homes were passed, indicating a growth rate of 13% year-over-year. 77.9 m U.S. homes were passed with fibre. 51.5% of all the nation’s unique homes and businesses are now passed with fibre. The data indicates that some 69 million locations in the USA are ‘unique’ fibre homes. About 9 m of these are passed by multiple providers.